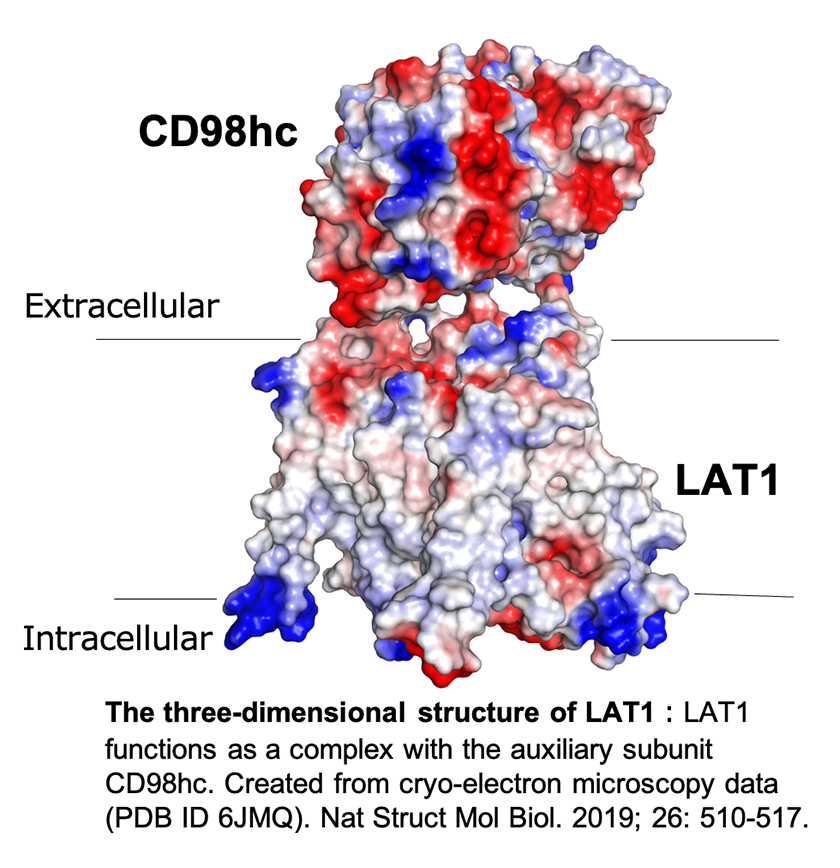
The Role of LAT1 in Cancer Biology
Cancer cells differ significantly from normal cells in their metabolic demands. To sustain their rapid growth and proliferation, cancer cells rely heavily on nutrient supply systems. LAT1 plays a key role in this process by transporting essential amino acids such as leucine and phenylalanine into the cells. These amino acids not only fuel protein synthesis but also activate mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) signaling, a pathway central to cell growth and metabolism.Importantly, LAT1 expression is highly elevated in many types of cancer, including pancreatic, lung, and brain cancers. This overexpression is strongly correlated with tumor aggressiveness, poor prognosis, and resistance to existing therapies, making LAT1 a compelling therapeutic target.
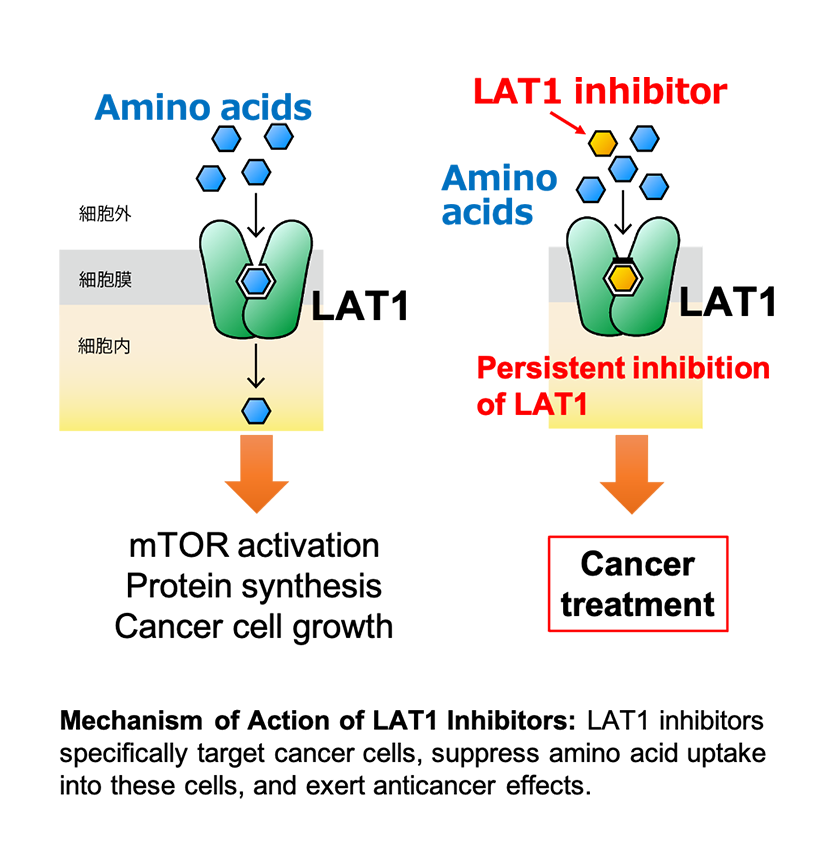
Mechanisms of Cancer Suppression Through LAT1 Inhibition
By inhibiting LAT1, we can strategically target cancer cells while sparing normal cells, as LAT1 is expressed at low levels in most healthy tissues. The therapeutic potential of LAT1 inhibition lies in its ability to:
Block Nutrient Supply
LAT1 inhibition disrupts the uptake of essential amino acids, effectively starving cancer cells of the nutrients required for growth and survival.
Suppress mTOR Signaling
LAT1 inhibition halts the activation of the mTOR pathway, a master regulator of cell proliferation and survival, thereby impairing cancer progression.
Induce Metabolic Stress
By depriving cancer cells of critical resources, LAT1 inhibition creates a state of metabolic imbalance, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis (programmed cell death).